HIV Testing in the United States
Key Facts
- HIV testing is integral to HIV prevention, treatment, and care. Knowledge of one’s HIV status enables individuals to engage in HIV treatment and is important for preventing transmission. While the share who know their HIV status has increased over time, as of 2019, 13% of people with HIV did not know they were HIV positive. Studies show that those who learn they are HIV positive modify their behavior to reduce the risk of HIV transmission and that those who do not know they are positive account for nearly 40% of new HIV infections.
- In 2019, fewer than half (43%) of nonelderly adults in the United States (U.S.) have ever been tested for HIV. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) recommends that everyone aged 13-64 be tested for HIV at least once as part of routine health care, and at least annual testing for those at higher risk.
- Early knowledge of HIV status allows for linkage to medical care and treatment that can reduce morbidity and mortality and improve quality of life. Treatment guidelines recommend starting antiretroviral treatment as soon as one is diagnosed with HIV. Individuals with HIV who have an undetectable viral load, achieved through used of effective antiretroviral therapy, cannot sexually transmit HIV to others.
- Most people with health insurance – both public and private – have access to HIV testing, often at no cost. And, for those without insurance, HIV testing can often be obtained at little or no cost in community settings.
| 1981: First AIDS case reported |
| 1984: Human immunodeficiency Virus (HIV) identified |
| 1985: First test for HIV licensed (ELISA) |
| 1987: First Western Blot blood test kit |
| 1992: First rapid test |
| 1994: First oral fluid test |
| 1996: First home and urine tests |
| 2002: First rapid test using finger prick |
| 2003: Rapid finger prick test granted CLIA (Clinical Laboratory Improvement Amendments) waiver |
| 2004: First rapid oral fluid test (also granted CLIA waiver) |
| 2006: CDC recommends routine HIV screening in U.S. health care settings |
| 2007: CDC launches Expanded HIV Testing Initiative in U.S. |
| 2007: WHO/UNAIDS global guidelines recommend routine HIV screening in health care settings |
| 2010: First test approved that detects both antigen and antibodies |
| 2012: First rapid oral fluid home test approved |
| 2013: USPSTF gives routine HIV screening an “A” rating |
| 2013: First rapid test approved that detects both antigen and antibodies, and distinguishes between acute and established HIV-1 infection |
| 2015: Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services announces Medicare coverage of annual HIV screening for all beneficiaries 15-65, and for those older and younger beneficiaries at “increased risk” for HIV |
| 2019: USPSTF reaffirms its “A” rating for HIV screening |
| 2021: HHS clarifies the USPSTF “A” grade for PrEP (pre-exposure prophylaxis), an HIV prevention drug, encompasses ancillary services including HIV testing, among others. |
Testing Statistics
- Through earlier detection, raising awareness of HIV status, and linkage to care and treatment, testing plays an important role in addressing the U.S. epidemic.
- Among the 2 million people with HIV in the U.S., an estimated 13% do not know they are infected and this share accounts for nearly 40% of new transmissions. Awareness of HIV status allows those who are positive to engage in HIV treatment, reduce viral load (the amount of virus in the body) and prevent transmission. Additionally, studies show that those who learn they are HIV positive modify their behavior to reduce the risk of HIV transmission.
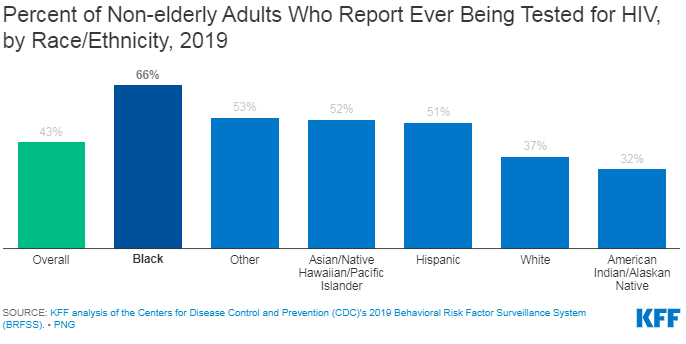
- According to the CDC’s Behavioral Risk Factor Surveillance System (BRFSS) in 2019, 4 in 10 (43%) U.S. adults, aged 18-64, reported ever having been tested for HIV (see Figure 1). HIV testing rates vary by state, age, race/ethnicity, and other factors. People of color report having ever been tested for HIV at higher rates than White people. For example, 66% of Black people and 51% of Hispanic people report ever having been tested for HIV compared to 37% of White people. (See Figure 1.)
- According to a 2014 survey of gay and bisexual men in the U.S., relatively few report being tested as regularly as is often advised. Seven in 10 say they have been tested at some point in their lives, 1 in 5 say they were tested within past six months, and 3 in 10 say they’ve never been tested for HIV, a share that rises to 44 percent among those under age 35. A more recent, 2020 study found that 39% of gay and bisexual men and men who identify as something other than heterosexual or transgender have been tested within the last two years.
- Findings from a CDC analysis of a decade of testing data suggests that some people at risk for HIV are not getting tested as frequently as recommended.
Testing Recommendations and Requirements
The U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) recommends everyone aged 13-64, receive at least one HIV test as a part of routine health care and more frequent testing, at least annually, for those at higher risk. Per the CDC, individuals who may benefit from at least annual screening include:
- sexually active gay or bisexual men (some of whom may benefit from more frequent testing, such as every 3 to 6 months)
- individuals who have had sex with an HIV-positive partner
- individuals who have had more than one partner since their last HIV test
- those who have shared needles or works to inject drugs
- people who have exchanged sex for drugs or money
- individuals who have another sexually transmitted disease, hepatitis, or tuberculosis
- those who have had sex with someone who has participated in any of the above activities or with someone with an unknown sexual history
Certain factors are known to reduce the risk of HIV transmission including condom use, antiretroviral treatment leading to durable viral load suppression among those with HIV, and the use of pre-exposure prophylaxis (PrEP) among those at increased risk for HIV.
Additionally, HIV testing is recommended for all pregnant women and for any newborn whose mother’s HIV status is unknown. Treatment provided to pregnant HIV-positive people early in pregnancy can reduce the risk of transmitting HIV to 1% or less. HIV testing is also recommended for anyone who has been sexually assaulted.
CDC recommends that all HIV screening be voluntary, and opt-out (patient is notified that the test will be performed and consent is inferred unless the patient declines) vs. opt-in (test is offered to the patient who must explicitly consent to an HIV test, often in writing).
HIV testing is mandatory in the U.S. in certain cases, including for: blood and organ donors; military applicants and active duty personnel; federal and state prison inmates under certain circumstances; and newborns in some states. As of January 2010, HIV testing is no longer mandatory for those wishing to emigrate to the United States or for refugees.
Insurance Coverage of HIV Testing
Most insurers now broadly cover HIV testing, many without cost-sharing, in part due to a decision made by the United States Preventive Services Task Force (USPSTF), an independent panel that assess the net benefit of preventive services and assigns a subsequent letter grade (A-D). Under the ACA, any “A” or “B” graded preventive services must be provided by most insurers without cost-sharing; in addition, traditional Medicaid programs, while not required to provide USPSTF top graded services, are incentivized to do so. In 2013, the USPSTF gave HIV screening an “A” rating for all adolescents and adults, ages 15 to 65. It also gave an “A” grade to HIV screening for pregnant women. Both of these recommendations were reaffirmed in 2019. The current insurance coverage landscape of HIV testing is as follows:
- Private Insurance: Most private plans cover HIV testing without cost-sharing. All plans created after the ACA was signed in 2010 must provide coverage aligning with the USPSTF “A” and “B” grades without cost sharing.
- Medicaid: All Medicaid programs cover “medically necessary” HIV testing and most cover routine HIV screening.
- Medicaid Expansion Programs: In addition to covering medically necessary testing, Medicaid programs expanded under the ACA are required to cover preventive services rated “A” or “B” by the USPSTF, including HIV screening, without cost-sharing. To date 39 states and DC have expanded their Medicaid programs.
- Traditional Medicaid Programs: While all Medicaid programs must cover “medically necessary” HIV testing, coverage of “routine” HIV screening is an optional benefit in traditional (non-expansion) Medicaid programs. Still, most states do cover routine HIV screening. In a 2021 survey, of 42 responding jurisdictions, 40 states and DC (41 total) reported covering routine HIV testing. Just one state, Florida, reported covering “medically necessary” testing. Nine states did not respond, including 3 that reported covering only “medically necessary” testing in a prior survey (GA, NE, and SD). As of November 2021, among the 42 states that cover routine HIV screening, 16 (CA, CO, DE, HI, KY, LA, MA, MT, NH, NJ, NV, NY, OH, OR, WA and WI) cover all USPTSF “A” and “B” graded services and have sought an additional 1% increase in their federal matching rate (FMAP) for these services under Sec. 4106 of the ACA.
- Medicare: In April 2015, following the 2013 USPSTF recommendation and a subsequent National Coverage Determination, CMS expanded Medicare coverage to include annual HIV testing for beneficiaries ages 15-65 regardless of risk, and those outside this age range at increased risk without cost-sharing. Additionally, Medicare will cover up to three tests for pregnant beneficiaries.
- Uninsured. For those without insurance coverage (or wishing not to use their insurance), HIV testing can be obtained at little or no cost in some community based settings (e.g., stand-alone HIV testing sites, community health centers, mobile testing clinics).
Testing Sites and Policies
HIV testing is offered at CDC-funded testing sites (accounting for about 2.5 million tests in 2019) and in other public and private settings, including free-standing HIV counseling and testing centers, health departments, hospitals, private doctor offices, STD clinics, and mobile testing units. The overall positivity rate at CDC funded test sites was 0.9% in 2019. The positivity rate for new diagnoses was 0.4% but was substantially higher for certain sub-populations (e.g. 1.5% for transgender people, 1.5% for men who have sex with men and 2.2% for men who have sex with men and also use injection drugs). Among CDC-funded testing sites, non-health care facilities have a higher rate of clients testing HIV-positive than do health care and correctional facilities.
All states/territories have moved to HIV name reporting (in addition to reporting AIDS cases) where a person’s name is reported to the state if they test HIV positive. The state then reports the number of unique positive HIV tests to CDC (no names or other personally identifying information are reported to CDC; only clinical and basic demographic information are forwarded). This is considered confidential HIV testing. There is also anonymous HIV testing offered at some testing sites where identifying information is not collected/reported.
Testing Techniques
HIV tests aim to detect the virus by looking for evidence of the body’s immune response (antibodies), proteins on the surface of the virus (antigens), or genetic material from the virus (RNA). Detectable antibodies usually develop within 3-8 weeks after infection but may take longer; the period after initial infection with HIV before detectable antibodies develop is the “window period.” In 2010, the FDA approved the first HIV diagnostic test that detects both antibodies and antigen, a component of the virus that triggers the production of antibodies. In 2013, the FDA approved the first rapid antigen-antibody test, the first test also to distinguish between acute and established HIV-1 infection. Tests for antigen allow for earlier detection of HIV because they can detect the virus before the body has mounted a response, although there will still be a window period of approximately two weeks after initial infection during which no test can detect the virus. RNA, or nucleic acid tests, which detect the virus itself in the blood, are also available, but not routinely used for screening. The test may be used in cases where there has been a high-risk exposure to HIV because they are able to detect the virus earliest in infection, as a follow-up test to a positive antibody or antigen test and are now recommended in certain cases as part of assessment for PrEP.
HIV diagnostics in the U.S differ based on type of specimen tested (whole blood, serum, or plasma; oral fluid; urine); how the specimen is collected (blood draw/venipuncture; finger prick; oral swab; via urination); where the test is done (laboratory; point-of-care site; at home); and how quickly results are available (conventional or rapid). The main types of tests are:
- Conventional Blood Test: Blood sample drawn by health care provider; tested at lab. Results: less than an hour to several days.
- Conventional Oral Fluid Test: Oral fluid sample collected by health care provider, who swabs inside of mouth; tested at lab. Results: a few days to two weeks.
- Rapid Tests: Whole blood finger prick or venipuncture; plasma; oral fluid sample collected depending on complexity of rapid test and individual administering test. Results: approximately 10 minutes. If test is negative, no further testing is needed. If positive, test must be confirmed with a more specific test through conventional method. Some rapid tests have been granted CLIA waivers which allow them to be used outside traditional laboratories.
- Self Tests: There are two approved self (or home) tests, one of which is performed with a finger prick finger with a lancet, placing drops of blood on treated card, and mailed to lab for testing. An identification number on the card is used when phoning for results; counseling and referral available by phone. Results: in approximately three days. The other is a rapid oral fluid test for home use. Results: approximately 20 minutes. Both home tests may be purchased from drug stores and online. Self-testing may help address some barriers to HIV testing, including barriers resulting from the COVID-19 pandemic that may make some people more hesitant to access in person health services.
- Urine Test: Urine sample collected by health care provider; tested at lab. Results: a few days to two weeks.
After an HIV Test
Following an HIV test, individuals who test positive can expect a confirmatory test and linkage to HIV care and treatment. It is recommended to initiate antiretroviral treatment as soon as possible after diagnosis. Doing so facilitates the best possible clinical outcomes for the HIV positive individual and is also a prevention opportunity, as once that individual has an undetectable viral load HIV cannot be transmitted to others. Individuals who test HIV negative but who are at high risk for the infection, may be referred to additional prevention services such as PrEP which can reduce the risk of HIV acquisition through sex by about 99%.